How does Trauma Affect the Body?
April 5, 2023
In how many ways can trauma truly affect the human body?
Trauma is something that every individual has experienced throughout their lifetime, whether they realize it or not. It can heavily affect the body in more ways than one, it can affect the body both mentally and physically. Trauma affects everyone differently, whether that be a one-time, multiple, or long-lasting event, it has a different impact on everyone. In some individuals, trauma can be so grand that it can present itself clearly in PTSD (post traumatic stress disorder). The impact of trauma can be subtle, or it can be extremely destructive. The way that trauma affects people differently can depend on many different factors, including, individual characteristics, and the type of event causing the trauma. Let’s take a deeper look at the world of trauma and the effects it can have on an individual.
Common Responses
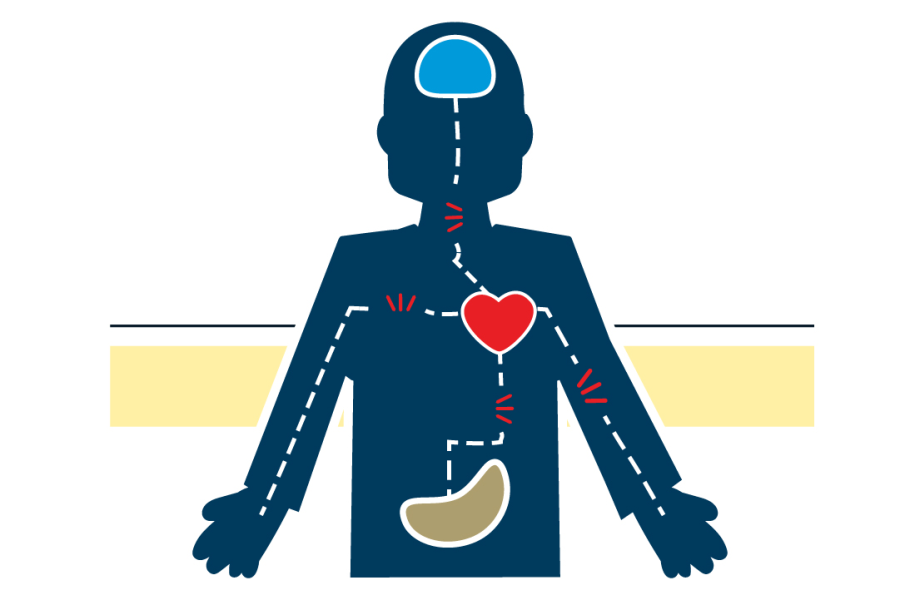
There are a variety of reactions that often present themselves in an individual experiencing a traumatic event. Survivors of traumatic events tend to exhibit immediate reactions, however, they can be typically resolved without long term or severe consequences. The majority of trauma survivors tend to develop coping strategies that help them deal with the aftermath and effects that the trauma holds over the individual. There are very many different responses to trauma. Two of those being physical and emotional. Emotional responses vary greatly by the socio-cultural history of the individual’s history. The main symptoms that show include anger, fear, sadness, and shame. Physical responses typically include somatic complaints, sleep disturbances, gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, musculoskeletal, respiratory, and dermatological disorders; urological problems; and substance use disorder.
Biology Behind Trauma
Trauma biology is an area of research that promises more complex and explanatory findings that have not been found yet. It is currently known that exposure to trauma of any kind can lead to biological changes and stress as well as stress responses. These biological problems are highly linked and associated with PTSD, and other mental illnesses. Things like serious accidents, physical assault, or abuse can cause for an individual to show signs of PTSD. For example, if an individual has suffered from abuse, neglect, and other brain-affecting traumas, it can increase an individuals vulnerability to encountering interpersonal violence throughout their lifetime. This can also potentially lead to the development of chronic diseases and physical and mental illnesses. This just goes to show that trauma and other illnesses have the potential to lead to and cause much bigger issues, such as biological issues.
Cognitions of Trauma
Along with biological changes that can result from trauma, there are also heavy types of cognitive/thought-processing changes that can happen due to trauma. These include…
- Cognitive errors: Misinterpreting current situations as dangerous because it triggers an old traumatic event
- Excessive or inappropriate guilt: An attempt to make sense of a situation and gain control over a traumatic event
- Idealization: Demonstrating inaccurate realizations, idealization, or justifications
- Trauma-induced hallucinations or delusions: Experiencing hallucinations or delusions that are congruent to that of the traumatic event at hand
- Intrusive thoughts and memories: Experiencing thoughts and memories associated with the trauma at hand, with no warning or reason
Trauma can have a very subtle to harsh effect on the body, both mentally and physically. There are many different symptoms and signs that come with living with trauma, and trauma is a very tricky type of disease on the body and the mind. Trauma can potentially lead to much bigger issues such as PTSD which is a very harsh and rough type of trauma. Trauma can present itself in many different individuals as well as in many different forms.